In consideration of the status of rail transit development in Shenzhen and the industrial challenges, the metro concentrates on crucial technological innovations such as ‘green and low-carbon, intelligent construction, smart metro operation, and Station-City integration,’ explains Xin Jie, Chairman of Shenzhen Metro Group.
The aim is to establish the brand image of ‘Green Shenzhen Metro, Smart Shenzhen Metro, and Technologic Shenzhen Metro,’ accelerate development into a world-class rail transit enterprise and provide valuable insights for the high-quality development of rail transit in the world
INTRODUCTION
With the continual evolution of societal contexts and technologies, the construction and operational principles of urban rail transit are undergoing adjustments and refinements. The shift extends from meeting the requirements of safety, functionality, and economy to green, intelligent, and high-efficiency, which are the needs of development in the new-era. In accordance with their respective characteristics and practical circumstances, different cities are actively exploring rail transit high-quality development pathways that are suited to their own needs.
As a crucial gateway for China’s reform and openingup and a core engine within the Guangdong-Hong Kong- Macao Greater Bay Area, Shenzhen considers the creation of a metro-city as an important strategic demand.
Commencing metro construction in 1998, Shenzhen has completed and operates 17 metro lines with an extensive network spanning 567km. This large-scale metro system essentially covers the core urban area as well as peripheral central regions, effectively supporting the sustained, rapid, and healthy socio-economic development of the city.

The Shenzhen Metro Group Co., Ltd. (abbreviated to Shenzhen Metro) actively explores development areas such as ‘green and low-carbon, intelligent construction, smart metro operation, and Station-City integration.’ Through the research and application of key technologies and the establishment of significant demonstration projects, continuous efforts are made to drive quality, efficiency, and dynamic transformations, leading to a significant enhancement of the enterprise’s technological innovation capabilities.
Driven by technological innovation, Shenzhen Metro is committed to creating a replicable and scalable innovative development model and achieving sustainable, high-quality development.
PROFILE OF SHENZHEN CITY AND SHENZHEN METRO COMPANY
Profile of Shenzhen City
Located in southern China, Shenzhen has a total area of 1,997.47km2 and a resident population of 17.66 million. Shenzhen is a strategic focal point in the Guangdong- Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area and a pioneering demonstration zone for socialism with Chinese characteristics. It serves as a window for China’s reform and opening-up.

Shenzhen is committed to establishing itself as a globally significant centre for advanced manufacturing, technological innovation, consumption, logistics, and finance. The city has achieved global attention for the phenomenon known as ‘Shenzhen speed’ and is acclaimed as the ‘Silicon Valley of China’. In 2022, the regional gross domestic product (GDP) of Shenzhen reached US$452.22 billion, with the total import and export volume for the year reaching US$516.62 billion, maintaining its position as mainland China’s leading city in export scale for 30 consecutive years.

Shenzhen embodies inclusive, open, and youthful vitality. Shenzhen is becoming a ‘global innovation centre”. It ranks second globally in the number of PCT international patent applications. As a pivotal transportation hub in the Asia-Pacific region, Shenzhen boasts an international deep-water port, large international airport, and the largest land port in Asia.
Major highways, national railways, and high-speed passenger lines converge here. With 24-hour customs clearance with Hong Kong, it takes only 20 minutes to reach the centre of Hong Kong from Shenzhen and 30 minutes to reach Hong Kong Airport. In 2023, the operational mileage of urban rail transit in the city reached 567.1km, ranking first in network density in China.

Profile of Shenzhen Metro
Shenzhen Metro is primarily responsible for the construction and operational services of the rail transit system in Shenzhen. It has established a comprehensive rail transit industry system and a sustainable development model, integrating national railways, intercity railways, and urban rail transit into a unified framework. Shenzhen Metro is dedicated to creating an open, innovative, and inclusive ‘rail transit ecosystem’.
The company adopts a ‘Four-in-One’ approach, encompassing rail transit construction, rail transit operation, Station-City development, and resource management. In recent years, Shenzhen Metro has consistently invested approximately US$13.96 billion annually in fixed assets. The total assets of the company amounted to US$99.7 billion in 2022.
Currently, ongoing projects include the metro, intercity railways, and national railway projects, with a total mileage of 625.9km. Shenzhen Metro continues to expand its brand influence, actively exporting diverse services such as operation, integrated commissioning, maintenance, and consulting to domestic and international (non-Shenzhen) routes, covering approximately 407.2km.

Shenzhen Metro adheres to the ‘entire life cycle management’ philosophy and has established a ‘one chain, two loops’ model based on the integration of ‘Rail + Property’. This has resulted in a self-sustaining operational mechanism that can generate profits without government subsidies. The ‘Rail + Property’ model is increasingly integrated with the city, with ‘Station-City integration’ projects, represented by transit hubs, gradually becoming core products.
Currently, a diverse product system, including office buildings, commercial spaces, hotels, advertising, and media, has been developed, covering approximately 1.3 million m2 of commercial area.
SHENZHEN METRO AND URBAN DEVELOPMENT
Rail Transit Supports the Rapid Development of Social Economy
Over the past four decades of China’s reform and opening-up, the socio-economic development of Shenzhen has maintained a level of high-speed growth.

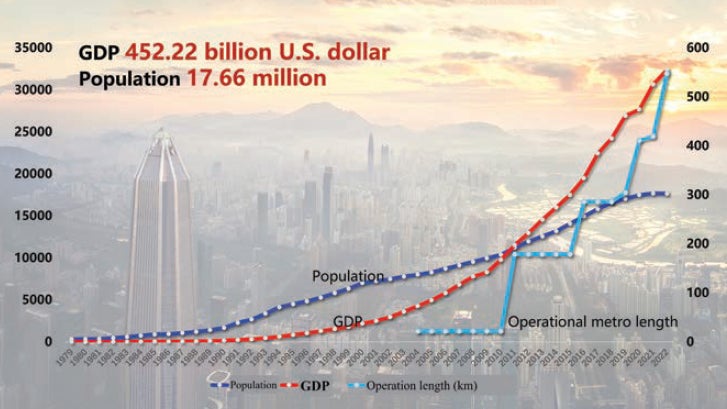
The regional GDP has increased from US$27.36 million in 1979 to US$452.22 billion in 2022. The urban area’s permanent population has steadily risen from 314,000 in 1979 to 17.66 million in 2022, as seen in Figure 2. Shenzhen has transitioned from being a fourth-tier city to joining the ranks of super-large cities during this period.
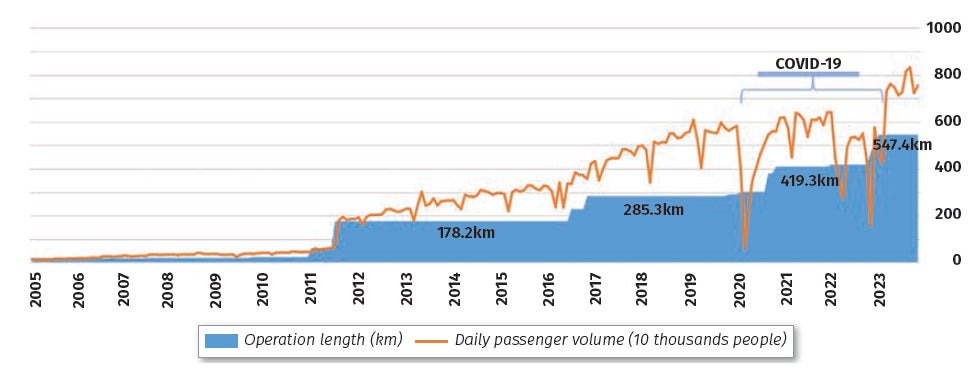
Since the initiation of rail transit construction in 1998, Shenzhen has completed and operates a vast metro network comprising 17 lines with a total length of 567km, with a daily passenger volume 8 million, peak daily10 million.
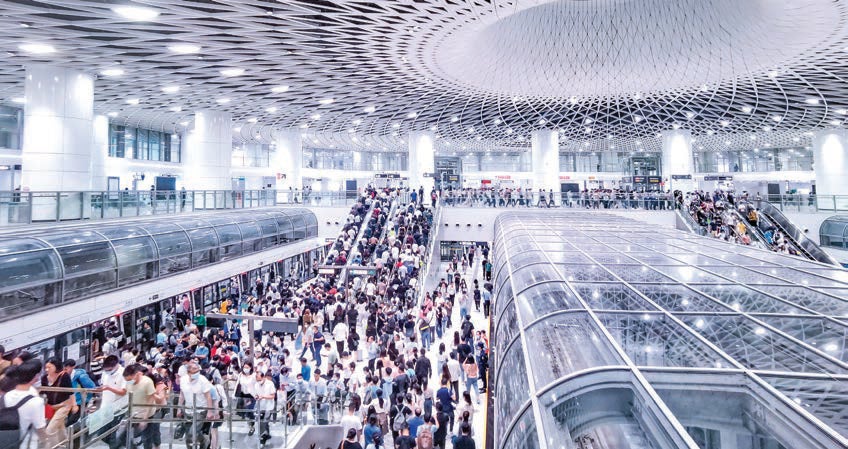

The rail network essentially covers the core urban area and peripheral central regions of Shenzhen, effectively supporting the sustained, rapid, and healthy socio-economic development of the city. Shenzhen’s urban rail transit operational mileage holds the top position among mainland Chinese cities in various aspects, including rail transit network density, passenger flow intensity, commuting convenience, smart mobility, comprehensive index of transit-oriented development (TOD), and volume of underground space development.
Rail Transit Guides the Orderly Expansion of Urban Space
Shenzhen Metro guides and supports the high-standard development and construction of the city, facilitating the transformation and upgrading of urban industries.

Currently, Shenzhen Metro has undergone four phases of construction and commenced the fifth phase in 2023. The first phase stimulated the development of areas such as Futian Central District and Chegongmiao District, while the second phase propelled the integration of the original Special Economic Zone both internally and externally. The third phase, with a focus on strengthening axes and cores, drove urban spatial development, and the fourth phase prioritised express lines, supporting the city’s eastward expansion strategy.
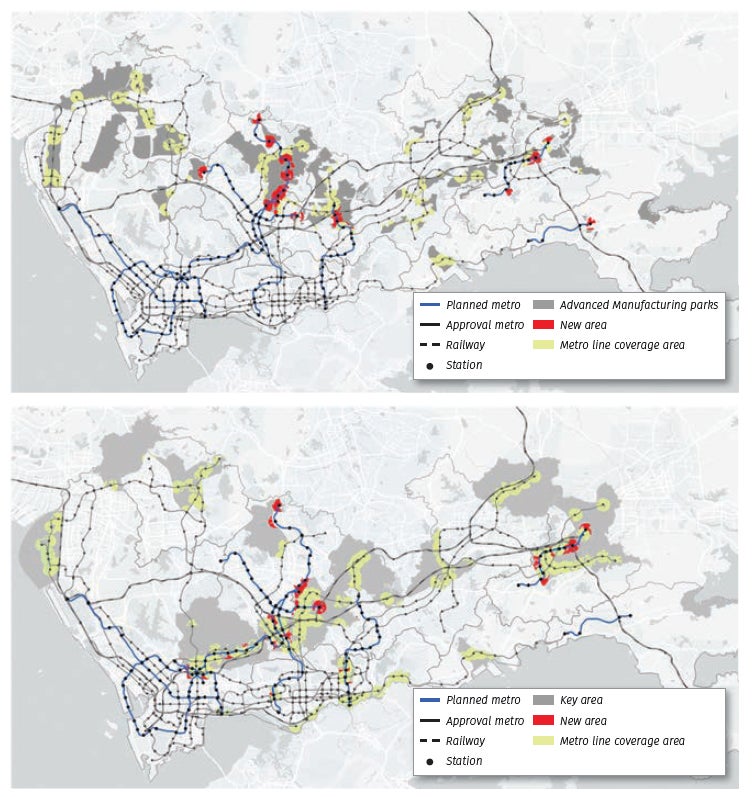
As of now, the metro system covers 18 out of 20 key city-level areas, with a land coverage rate of 74% for rail station construction in key areas within the central district and approximately 38% outside the central district. The fifth phase will further enhance coverage of national strategic platforms, such as the Qianhai Cooperation Zone and Guangming Science City, and strengthen rail transit support services for 20 key areas and 20 advanced manufacturing parks, as seen in Figure 3.
Rail Transit Supports the Optimization of Citizens’ Travel Structure
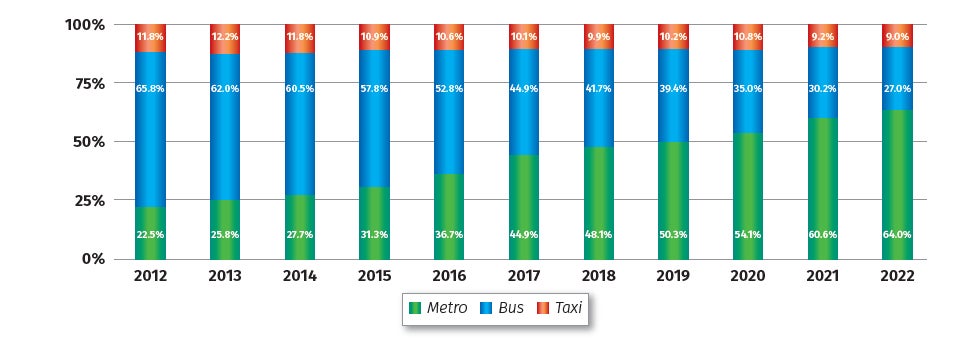
Shenzhen Metro played a crucial supporting role in the travel of residents, maintaining a rapid growth trend in the daily passenger volume of the entire metro network. The first phase of the project was completed and operational in 2005, with a peak daily passenger volume exceeding 200,000. In 2016, the daily passenger volume of the entire network gradually surpassed 4 million. Following the opening of the fourth phase of the project in 2020, the proportion of rail transit in public transportation exceeded 71%. In 2023, the daily passenger volume of the metro network surpassed 8 million, with the highest daily ridership reaching 10.17 million, as seen in Figure 4 and 5.
Shenzhen Metro also has established effective coverage of the residential population and employment positions in Shenzhen. Within an 800m radius of metro stations, the coverage ratio of residential population and employment positions is 44%. It is anticipated that by 2025, the coverage rate will increase to 58%, and after the completion of the fifth phase of construction in 2030, it will grow to 65%. This will essentially cover high-density population areas across Shenzhen, and the daily passenger volume is expected to exceed 10 million people.
EXPLORATION OF INNOVATION AND DEVELOPMENT
As the scale of metro construction and operation continues to expand, Shenzhen Metro faces challenges in various aspects such as funding, technology, and the environment. Through leveraging city’s location advantages, it urgently needs to enhance technological innovation capabilities and seek sustainable paths for high-quality development.
In terms of metro construction, investment in rail transit construction is continuously increasing, and key technologies in survey and design, engineering construction, and operations and maintenance need enhancement and breakthroughs. In terms of technical equipment, early operated metro lines will enter a period for equipment maintenance and upgrade.
Therefore, there is a need for technical innovation to elevate the intelligence in urban rail transportation, such as for equipment operation and maintenance, emergency response management, security risk prevention, etc. In terms of transportation organisation, the overarching goal should be the overall efficiency and effectiveness of metro lines. It is essential to strengthen technical innovation in transportation organisation, optimise transportation organisation models, and enhance the accessibility, emergency capabilities, and adaptability to passenger flow pressure of the lines.
Based on its extensive technological application scenarios, Shenzhen Metro will focus on the critical technological aspects of industry, collaborating with upstream and downstream enterprises to drive independent technological innovation. It aims to develop cutting-edge rail transit technologies, establish industry-leading technological assets, and achieve an upgrade in development models. Effective exploration and practices have been carried out in four areas: green and low-carbon technologies; mechanised modular construction; digitalisation and intelligent technologies; and, Station-City integrated development.
GREEN AND LOW-CARBON TECHNOLOGIES
Land-intensive Construction Concept and Technology
Shenzhen Metro implements the land-intensive concept and has developed key technologies for land-intensive metro construction. In the construction of Shenzhen Metro Line 7, an abandoned quarry was utilised to build the Shenyun Train Base. Simultaneously, facilities such as a cultural and sports park, metro command and control centre, and metro training centre were constructed on the train base. This integration harmonises with the Tanglang Mountain Country Park, transforms waste into valuable resources and achieves a harmonious unity between ecology and functionality.
Building Train Base with Sponge City Concept
Shenzhen Metro pioneered the integration of the sponge city concept with rail transit construction in China, applying it to the construction of metro train base and creating the concept of an ‘Ecological Train base’. Measures such as rain gardens, green roofs, elevated flower beds, and multi-functional retention ponds (scenic lakes) were implemented in the construction of the ‘sponge train base’. This innovative approach has been successfully applied in bases such as Changzhen base and Liangmaoshan base, achieving an annual runoff control rate exceeding 70% and contributing to an annual water conservation of over 5000 tonnes through precipitation storage.
Reduction and Harmless Muck Treatment
Shenzhen Metro has addressed the challenge of disposing of shield tunnelling muck, comprehensively promoting recycling and reduction. A total of 84 sets of equipment for shield tunnelling muck reutilisation have been established, generating approximately 3.5 million m3 of sand and gravel resources. This initiative has reduced the occupation of over 1,150 acres of abandoned muck and more than 30,000 tonnes of carbon emissions. The approach was honoured with the ‘Beyond Engineering’ Award by the International Tunnelling Association (ITA).
New Energy Utilisation with ‘Rail + Photovoltaic’ Model
Firstly, installing solar photovoltaic power generation systems at elevated metro stations. The distributed photovoltaic generation can meet approximately 30% of the power demand for lighting at elevated stations on Shenzhen Metro Line 6, and during peak generation periods, it can even supply over 80% of the electricity demand.
Secondly, installing solar photovoltaic power generation systems at comprehensive transportation hubs.
The distributed photovoltaic system at the Shenzhen North Station hub has an installed capacity of 3.2MW, which can generate 3 million kWh annually, and a 1MW energy storage system is complemented.
Thirdly, installing solar photovoltaic power generation systems on the roofs of entrances and exits of metro stations. Installation has already been carried out at Shenzhen Metro Line 10.
Rail + Logistic
Based on the transportation hubs and metro lines, Shenzhen Metro has explored and researched the ‘Metro + Logistic’ model. With the ‘hub-to-station’ approach, logistics joint transportation has been implemented between Futian Transit Hub and Bihaiwan Metro Station on Line 11, and the Shenzhen SF Express Airport Base. This initiative has established a new model integrating modern rail transit with logistics facilities, achieving seamless intermodal transportation between air and metro.
Other Energy Conservation and Carbon Emission Reduction Measures
1 – Train regenerative inverter feedback system
Shenzhen Metro closely aligns with the industrial orientation of energy conservation and emission reduction in China, responding to the construction of an energy-saving society. Currently, Shenzhen Metro has installed 81 sets of train regenerative inverter feedback absorption devices, saving an average power of 9,700 kWh/day, promoting industrial restructuring, and the development of strategic industries.
2 – Permanent magnet synchronous traction system
The permanent magnet synchronous traction motor adopts a fully enclosed structure to reduce electromagnetic noise. Compared to asynchronous motors, its rated power is higher, especially in the high-efficiency range, and the volume and weight of permanent magnet synchronous traction motors with the same capacity can be reduced by about 30%. The average energy consumption per train-kilometre for Shenzhen Metro trains using the permanent magnet traction system is 25% lower than that of trains using the asynchronous traction system, achieving a 25% energy saving rate.
3 – Efficient intelligent environmental control System
Shenzhen Metro’s efficient intelligent environmental control system is based on cloud platforms for equipment development, Building Information Modelling (BIM), deepening design, energy-saving control strategy optimisation, and the establishment of six standard systems, and achieve the energysaving goal of environmental control machine room efficiency (COP5.0, TCOP3.5). Compared to earlier operational metro lines, the total power consumption of the air conditioning system in newly constructed metro lines can be reduced by around 40%, and the total power consumption of stations can be reduced by about 30%. This holds significant demonstration value for accelerating low-carbon and green rail transit construction in the urban rail transit industry.
4 – Reducing the scale of metro stations
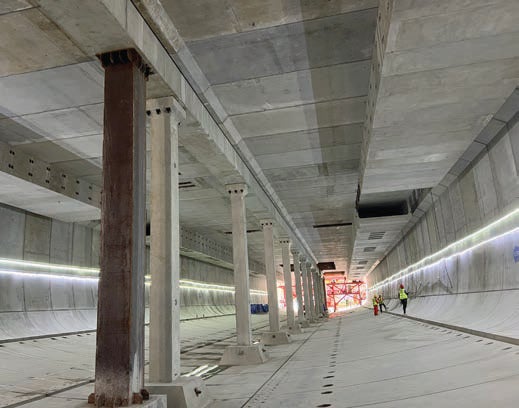
Shenzhen Metro has explored and studied the optimisation of metro station construction scale and electromechanical schemes, optimised station space through system upgrades and changes in operational modes. In the construction of the fifth phase of new lines, a comprehensive implementation of station and base scale reduction was carried out. For example, the standard station length for the 6A train set was optimised from 216m to 189m, resulting in a reduction of approximately 12% in the station’s main building area and a decrease of about 700 tonnes of carbon emissions.
MECHANISED AND MODULAR CONSTRUCTION
EPB-TBM Dual-mode Shield Tunnelling
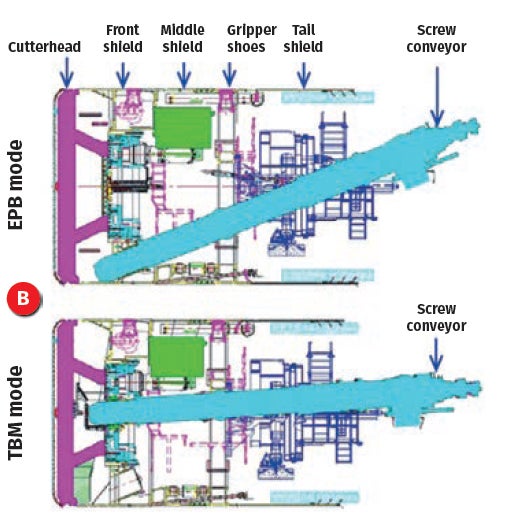
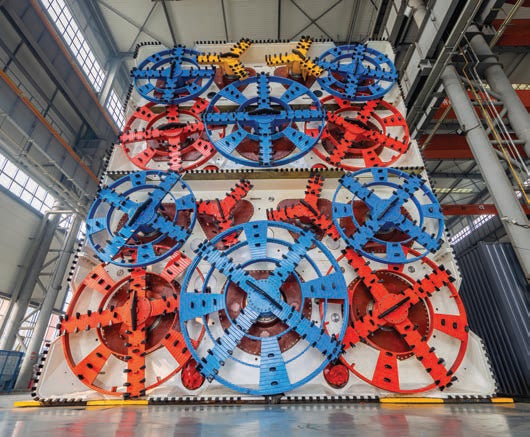
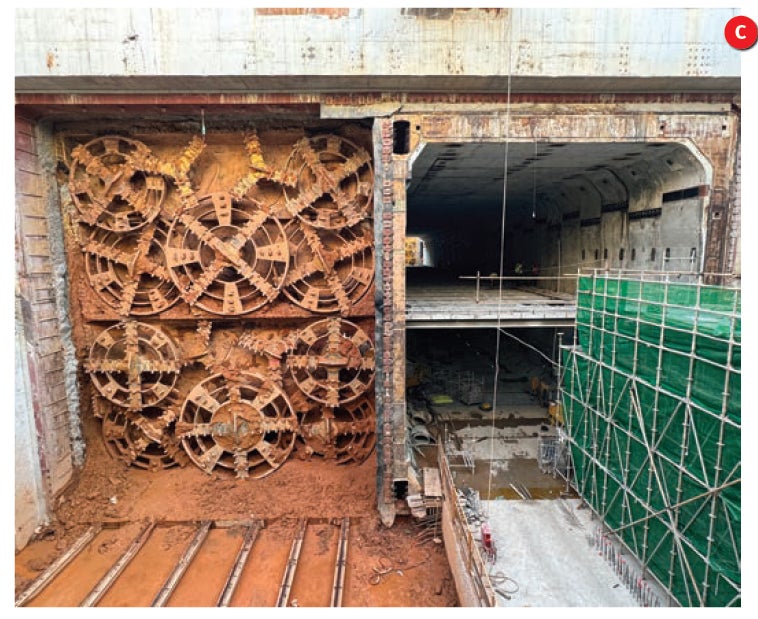
In ground where the soil and hard rock alternate, traditional earth pressure balance (EPB) tunnel boring machines (TBMs) exhibit low efficiency. Shenzhen Metro has explored the application of the EPB/TBM dual-mode shield machine to address this issue, as seen in Figure 6. Related equipment manufacturers are China Railway Engineering Equipment Group Co., Ltd., China Railway Construction Heavy Industry Co., Ltd. and so on.
Since 2018, a total of 71 dual-mode shield machines with diameters ranging from 6.48m to 9.1m have been gradually deployed in metro tunnel construction in Shenzhen. In TBM mode, two excavation methods, central belt conveyor and central screw, have been employed. The advance rate has increased by 30% compared to conventional EPB methods, with a 35% reduction in cutter consumption.
By establishing an adaptability assessment methodology for EPB/TBM dual-mode shield method, Shenzhen Metro has developed an intelligent selection platform for the machines. This platform enables intelligent selection based on factors such as geological parameters, construction period, and cost. Simultaneously, the mode-switching process for EPB/ TBM dual-mode shield machine has been optimised, with the fastest mode transition compressed to 10 days.
A Metro Station Construction Method by Large-diameter Shield Machine
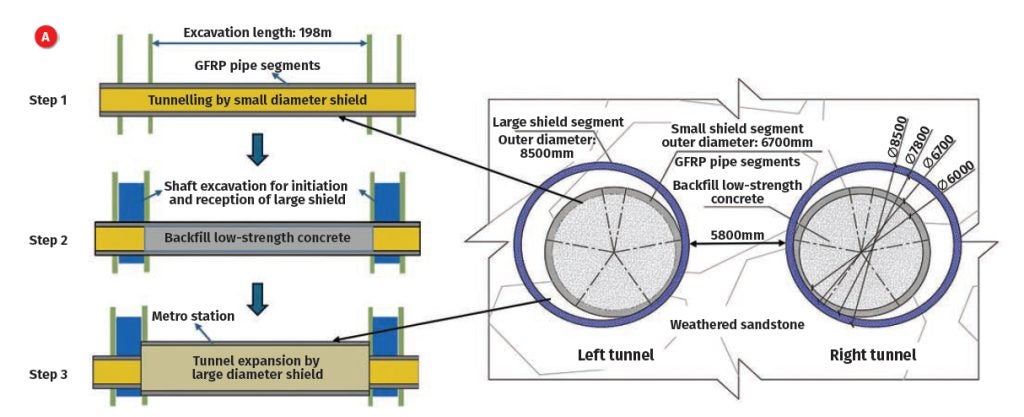
To address the issue of delayed subway openings caused by the addition of new stations, a construction method utilising large-diameter shield machines for station enlargement was proposed. This method was first applied to the Zhangbei Station on Shenzhen Metro Line 14 (Designer: China Railway Design Corporation, contractor: Construction Engineering Company of China Railway No.5 Engineering Group Co., Ltd, machine manufacturer: China Railway Construction Heavy Industry Co., Ltd.). In this approach, a small-diameter shield machine first passes through the newly added Zhanbei Station, glass fibre reinforced plastic (GFRP) segments were employed for lining the tunnel, which was then backfilled with low-strength concrete.
Subsequently, a large-diameter shield tunnel is utilised to cut and excavate the original GFRP segment, forming a large-diameter tunnel at each end, followed by the excavation of vertical shafts. Subsequently, a largediameter shield machine was inserted in the shafts for secondary excavation through the smaller bored tunnel, resulting in the creation of a side-platform station, as seen in Figure 7. Compared to traditional methods, this approach reduces the construction period by 10 months.
PREFABRICATED METRO STATION WITH INTERNAL SUPPORT SYSTEM
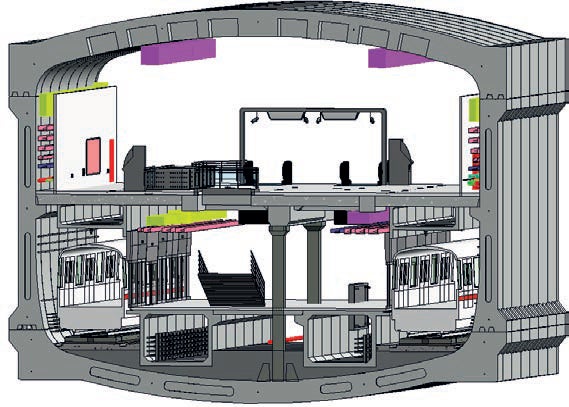
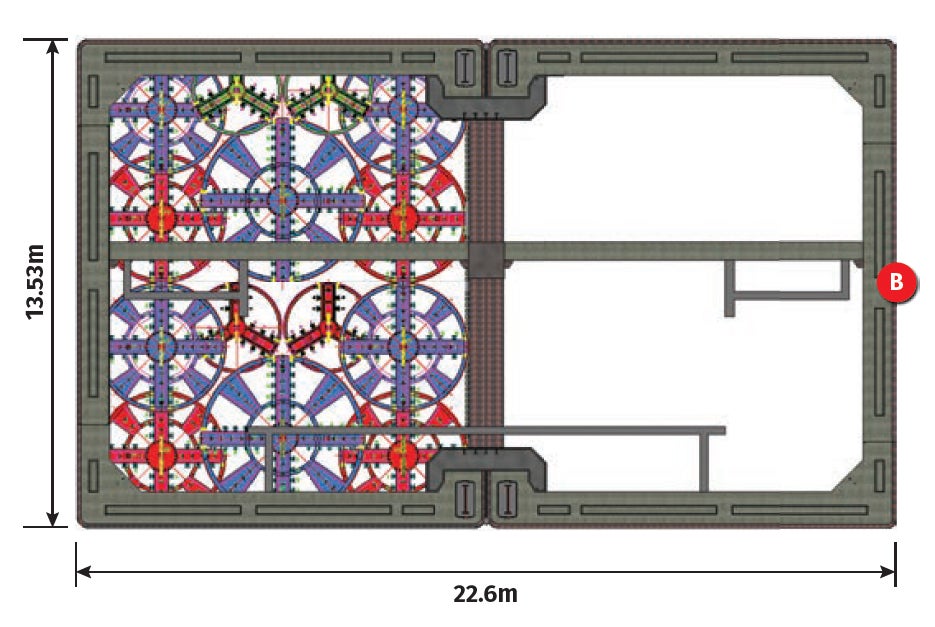
Shenzhen Metro innovatively applied fully prefabricated underground metro station technology. The station hall adopts a column-free arch structure, and the complete structure is assembled from four structural segments. Internal structures such as the platform slab and stairs are also constructed using prefabricated methods. The Shapu Station on Shenzhen Metro Line 12 is the first station to adopt this technology (Designer: Shenzhen Municipal Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd., contractor: Sinohydro Bureau NO.7 Co., Ltd.), as seen in Figure 8. Compared to traditional metro station construction, the construction period of fully prefabricated stations is reduced by 4-6 months, while simultaneously reducing labour by approximately 80% and temporary steel usage by 800 tonnes. For the section with tunnel tracks, prefabricated track slabs were used, resulting in a 30% reduction in manual labour and a 20% improvement in efficiency compared to traditional track construction, leading to a reduction of approximately 3 tonnes/km of carbon emissions.
A Metro Station Construction Method by Combination Pipejacking
Shenzhen Metro has developed a new type of tunnelling construction equipment – the world’s largest excavation area for a rectangular pipejacking machine (width 11.29m × height 13.55m). The innovative approach involves the application of a combined rectangular pipejacking machine for constructing the main structure of metro station, as seen in Figure 9, and the Shasan Station on Shenzhen Metro Line 12 serves as a demonstrative project for this technology (Designer: Shenzhen Municipal Design and Research Institute Co., Ltd., contractor: Sinohydro Bureau NO.11 Co., Ltd, machine manufacturer: China Railway Engineering Equipment Group Co., Ltd.). This marks the first introduction of an extra-large section combined rectangular pipe jacking machine into the metro station construction, resulting in a reduction of effective construction period, lowered comprehensive investment costs, and an effective resolution of the conflicts between large-scale construction of metro and the vibrant urban environment, economic development, and social harmony. The project has completed tunnelling and achieved an advance rate of 1m/day.
Prefabricated Construction of Metro Equipment Room and Pipeline All metro station cooling equipment rooms, utility rooms, pipelines, escalators, and tunnel ventilation ducts were constructed using prefabrication techniques in Shenzhen Metro, with the materials pre-processed in factories. This approach reduces material waste generated from secondary processing and significantly minimises on-site operations.
DIGITAL AND INTELLIGENT TECHNOLOGIES
Digitisation of Management Process
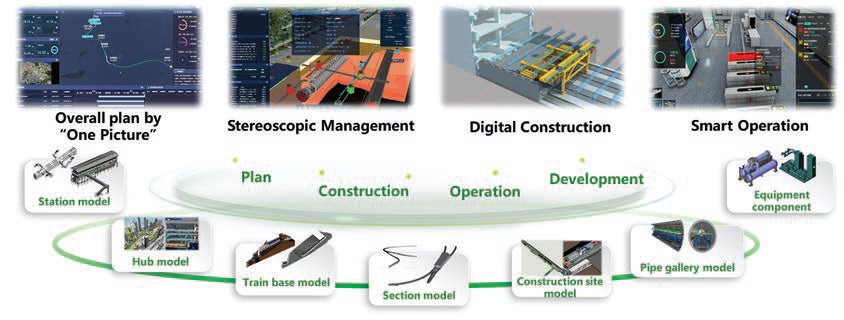
To advance Shenzhen Metro’s digital transformation of management, a total of 88 key management processes have been fully digitised. Through an information platform, connections have been established among design, construction, supervision, equipment suppliers, and other units. Digital control over processes have been achieved, such as investment, progress, acceptance, and records. In the past three years, participating units have collectively logged in over 18 million times, processed nearly 1 million event workflows, and circulated 8TB of data with 160 million records online.
BIM Application within Entire Life Cycle
Shenzhen Metro is comprehensively advancing the application of BIM/CIM (City Information Modelling) technology, actively exploring 39 intelligent application scenarios throughout the entire lifecycle of rail transit. Over 9,300 BIM models have been created, and a repository of 22,000 BIM components has been accumulated, forming a BIM/CIM ecosystem. During the planning phase, BIM+GIS integration of elements such as reality, geology, underground structures, and pipelines is employed to deduce the feasibility of the overall route planning. In the design phase, BIM forward design is promoted to optimise design solutions. During the construction phase, BIM is applied to progress and investment management, quality, and safety control, create intelligent construction sites. QR codes are utilised to link equipment with BIM models, and the digitisation of BIM handovers is advanced.
Rail Transit Line Network Cloud Technology
To support the comprehensive construction of the cloud and smart metro, the Shenzhen Metro Line Network Cloud Platform and Big Data Centre have been built, and IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS platforms have been established. Resulting in the transformation and upgrading of the Shenzhen Metro towards fully digital and intelligent operations. Shenzhen Metro firstly used line-level cloud computing in the world, constructed a comprehensive cloud-based platform for metro lines based on cloud computing technology, which hosted production business systems such as signaling, comprehensive monitoring, security, and passenger information. Each metro station reduces server, storage, workstation, and network equipment space by 100m2.
Smart Metro Operation Technology
The intelligent transformation of Airport Station and Shenyun Station on Metro Line 11 has been initiated. To address operational challenges, enhance passenger service quality, and improve station management efficiency, a smart transportation and passenger service system with the characteristics of ‘integration, convenience, precision, safety, and green’ has been established.
Metro Line 20 focused on four aspects: safety; efficiency; energy conservation; and, economy. It is coordinated by the intelligent ‘train brain’ and comprises four intelligent systems: Intelligent Security System; Intelligent Evacuation System; Smart Passenger Flow Analysis System; and, Centralised Control System. This collectively forms a smart metro station. The trains in Metro Line 20 can operate in the optimal mode with more precise control by incorporating fully automatic train operation technology and full coverage of 5G signal.
Fully Automatic Driving System of the Train
Shenzhen Metro continues to enhance fully automated driving technology, employing the highest level of GoA4 automated driving systems in all newly constructed lines. Metro Line 20 is the world’s first passenger-carrying operational line using train-to-train communication autonomous operation technology. It incorporates TACS to enable GoA4 level fully automatic operation in a single launch. This technology is at the leading level in the industry.
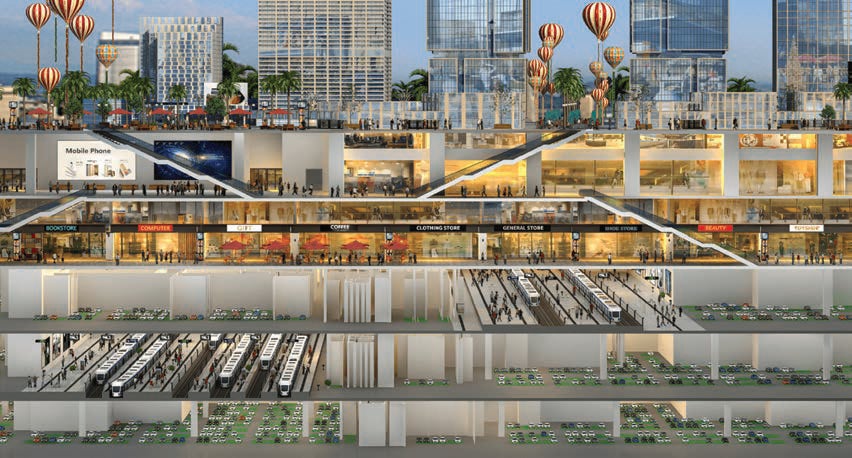
STATION–CITY INTEGRATED DEVELOPMENT
Development of the Overhead Property in the Rail Transit
Shenzhen Metro has innovatively proposed the concept of ‘Metro Domain Stereoscopic Space’, forming a complete set of technologies for integrated planning and design of transit hubs and overhead properties, as well as comprehensive utilisation of above ground and underground spaces, as seen in Figure 11. Qianhai Hub is a super project integrating transportation hub and urban complex with 3 metro lines and 2 intercity lines. Total construction area is about 2 million m2. The estimated daily passenger volume is expected to reach 750,000.
China’s first ‘Structural Design Standards for Overhead Buildings on Rail Transit Train Bases’ was compiled to address the scarcity of land resources in ultra-large cities. The design standard for ‘Full-Frame Shear Wall Structure’ was proposed, it allows for the construction of overhead buildings on train bases with a height exceeding 120m. As of the end of 2023, the total construction scale of transit-oriented development (TOD) reached 17.42 million m2, with 5.71 million m2 completed and 11.71 million m2 under construction.
Typical Metro Transit Hub Project
1 – Gangxia North Transit Hub
The Gangxia North Transit Hub, where five metro lines converge, spans a total underground construction area of 243,800m2. The transit hub integrates underground spatial systems, municipal functions, rail transit, cultural landscapes, and other elements, employing an integrated design and construction approach. It achieves multi-level spatial openness and integration of platforms, track areas, concourses, and urban overpass corridors.
In the open-cut underground structure, a world-first 48m×51m span steel structure is utilised, and the design incorporates the ‘Eye of Shenzhen’ concept to bring natural light into the underground station platforms, as seen in Figure 12.
2 – Huangmugang Transit Hub
The Huangmugang Transit Hub is China’s first integrated ‘Bridge, Station, and Tunnel’ transportation hub, serving as an exemplary model for ‘Transportation Integration, Functional Integration, and Spatial Integration’ in urban underground space development. The transit hub ingeniously suspends the three-lane tunnel structure beneath the station structure’s roof, meeting the linear design requirements of the tunnel’s phased curves. This integration harmonises paths, buildings, and structures, releasing the lower space and effectively utilising the increased net clearance, as seen in Figure 13. The project was awarded the ‘Underground Space Innovation Contribution’ Award by ITA in 2022.
SUMMARY AND PROSPECT
Shenzhen Metro adheres to the development philosophy of ‘Innovation, Coordination, Green, Openness, and Sharing’. It deeply implements the innovation-driven development strategy, fully plays the role of enterprises as innovation leaders. Shenzhen Metro has conducted a series of critical technological innovations in areas such as ‘green and low-carbon, intelligent construction, smart metro operation, and Station-City integration’. These innovations have been actively applied, with several significant technological achievements reaching a leading level in the world.